Thursday, 6 May 2010
Print protected pdf
Open the new pdf for example with Acrobat Reader and you can print.
pdf2ps protected.pdf unprotected.ps
ps2pdf unprotected.ps unprotected.pdf
Wednesday, 17 February 2010
How format pendrive with fat32 File System
sudo fdisk -l
2. Create a fat32 FS:
mkfs -t vfat /dev/sda
Monday, 15 February 2010
Share Internet between Ubuntu and VmWare Windows
It's working.
Saturday, 13 February 2010
How to view Quicktime videos
Code:
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
Saturday, 12 December 2009
Uninstall netbeans 6.5.1
cd ~/netbeans-6.5.1
./uninstall.sh
Tuesday, 17 November 2009
Ubuntu 9.10 vmware arrow key
xkeymap.nokeycodeMap = true
to /etc/vmware-server-console/config or ~/.vmare/config
and restart console/player.
There is no need to restart vmware server.
Tuesday, 6 October 2009
Checking Disk Space From Gnome and Ubuntu
To access Disk Usage Analyzer in Gnome, click on Applications \ Accessories \ Disk Usage Analyzer
When launched, DUA will start up in a stand by state, showing you total system capacity, used and available disk space.
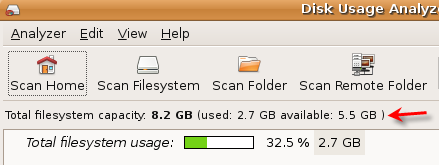
To view the entire file system including usage by individual directories, click the Scan Filesystem icon on the toolbar. When the scan is completed, the full tree of your file system will be displayed.
From this display, you get a nice picture of the disk usage on the entire file system. You can also expand the top level directories and drill down to see sub-directoires and their disk usage, and sort each column to view each directory usage, size and contents. In the right window pane, a graphical layout is displayed. Moving your mouse over a block will display the directory and size.
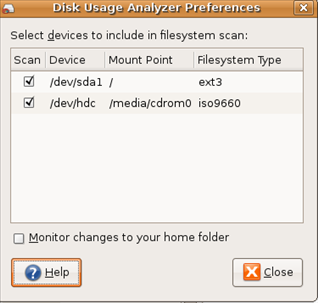
Selecting Edit \ Preferences from the menu, allows selection of any additional devices connected to your Computer that can be enabled or disabled from being monitored.
A feature that I like with Disk Usage Analyzer, is the ability to right click and open the directory by launching Nautilus File Browser.
Checking Disk Space From The Command Line
Another way to view disk usage in Ubuntu is from the Terminal window by clicking on
Application \ Accessories \ Terminal from the panel in Gnome.
Unlike Windows, finding available disk space, from the command prompt, is much easier in Ubuntu using the df command when connected locally or remote via an SSH session.
DF command reports how much free disk space is available for each mount you have. When executing
DF, I like to use the -h option, which returns the output in a more readable format:
greg@lt1:~$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda5 116G 61G 50G 56% /
tmpfs 1.5G 0 1.5G 0% /lib/init/rw
varrun 1.5G 148K 1.5G 1% /var/run
varlock 1.5G 4.0K 1.5G 1% /var/lock
udev 1.5G 176K 1.5G 1% /dev
tmpfs 1.5G 412K 1.5G 1% /dev/shm
lrm 1.5G 2.2M 1.5G 1% /lib/modules/2.6.28-15-generic/volatile/dev/mapper/truecrypt1
DF can also report free disk space for individual directories by entering the following command at the prompt:
ds -h /nameofdirectory
Using df at the command prompt is most usefull when checking disk space on remote computers.
To view more available options with df, enter df –help at the command prompt.
-
Step 1. Installing Docker # Add Docker's official GPG key: sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl sudo instal...
-
/etc/locale.gen uncoment en_GB.UTF-8 en_US.UTF-8 run locale-gen as root
-
sudo apt -y install wget wget https://zoom.us/client/latest/zoom_amd64.deb sudo apt install ./zoom_amd64.deb

